The Future of Wood-Plastic Composites in a Low-Carbon Economy
As the world shifts towards a low-carbon economy, industries are actively seeking sustainable and eco-friendly materials to replace traditional, resource-intensive options. One of the most promising alternatives is wood-plastic composite (WPC)—a material that blends recycled plastic and wood fibers to create durable, long-lasting products. This rapidly growing industry aligns with government policies promoting environmental sustainability and circular economies. With strong support and continuous technological advancements, WPC materials are now approaching international standards in quality and performance.
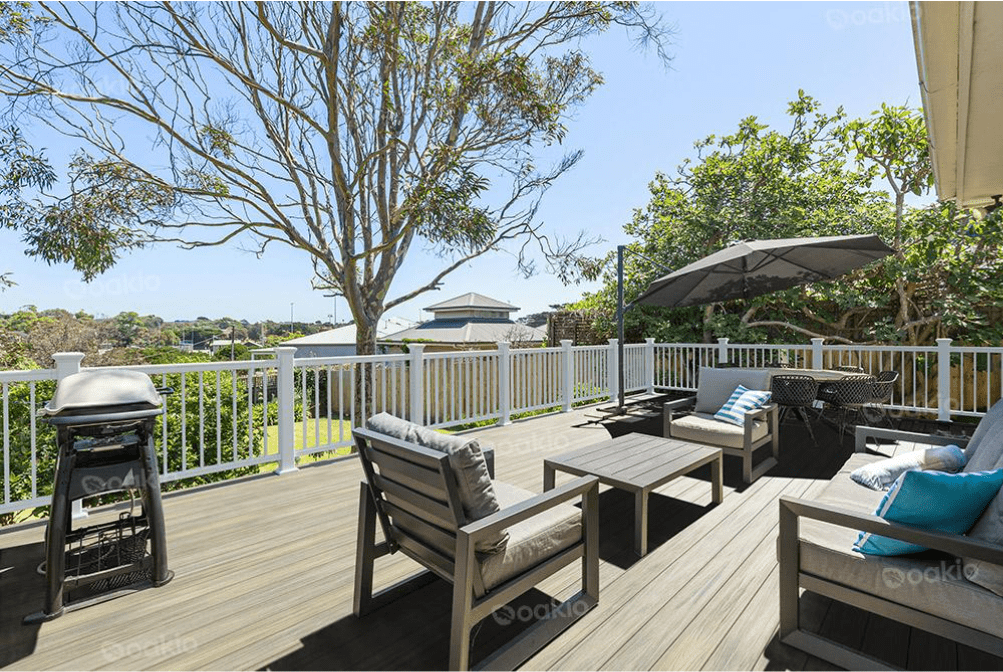

WPC has already found widespread applications in construction, decoration, packaging, and specialized industries, replacing traditional materials such as wood, plastic, metal, and aluminum. As its annual production continues to increase, its market potential expands, making it a key contributor to a more sustainable future.
The Role of WPC in a Sustainable Future
Growing environmental awareness has led to an urgent need for resource recycling and waste reduction. Plastic waste remains a major environmental challenge, with billions of tons accumulating in landfills and oceans each year. WPC provides an innovative solution by repurposing plastic waste into high-performance materials, reducing environmental pollution and promoting circular economy principles.
Moreover, WPC materials offer long-lasting durability, reduced maintenance needs, and improved resistance to weathering, moisture, and pests—advantages that make them superior to traditional wood in many applications. In regions where deforestation is a concern, WPC can serve as an effective substitute, reducing the demand for timber and helping to preserve forests.
Despite its advantages, the WPC industry is still in its early stages in many regions, with huge growth potential waiting to be tapped. As more industries recognize the benefits of WPC, its applications are expected to expand, further solidifying its role in sustainable development.
Key Trends in WPC Development
The future of WPC is shaped by continuous technological advancements and evolving market demands. Five major trends are driving its development:
1. Diversified Raw Materials
Innovation in raw materials is expanding the capabilities of WPC products. The industry is now incorporating a wider variety of fibers, additives, and reinforcements, including bamboo, rice husks, and other agricultural byproducts. These additions enhance material properties, such as strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental stressors, allowing for a broader range of applications.
Moreover, advances in bio-based plastics and biodegradable additives are being explored to make WPC even more sustainable. These innovations will help reduce reliance on fossil fuel-derived plastics, making WPC a truly green building material.
2. Intelligent Manufacturing
The adoption of smart manufacturing technologies is transforming WPC production, making it more efficient, precise, and sustainable. Advanced techniques such as 3D printing, automation, and full-capping co-extrusion are revolutionizing the industry.
3D printing technology allows for customized WPC products with intricate designs and minimal material waste.
Co-extrusion technology enhances WPC’s surface protection, making it more resistant to fading, staining, and scratching.
Automated production lines improve consistency and efficiency, reducing labor costs and enhancing overall product quality.
As manufacturing continues to advance, WPC products will become more affordable and accessible, accelerating their adoption in global markets.
3. Standardization and Quality Control
With WPC gaining prominence in construction and infrastructure projects, the need for standardized manufacturing processes and quality regulations is growing. Many countries are now implementing national and international standards to ensure consistency in performance, safety, and environmental impact.
Standardization benefits manufacturers, suppliers, and consumers alike by:
Ensuring compatibility between different WPC products and components.
Improving reliability and long-term performance.
Building trust among architects, contractors, and end-users.
As regulations evolve, manufacturers that adhere to strict quality control measures will gain a competitive edge in the market.
4. High-Value Applications
Traditionally, WPC has been used for decking, fencing, and cladding. However, the industry is now shifting towards higher-value applications that go beyond construction. By integrating WPC with other advanced materials, researchers and manufacturers are developing stronger, more versatile composite products for industrial use.
Emerging high-value applications include:
Structural components for bridges and public infrastructure.
Fire-resistant and anti-slip materials for commercial and industrial flooring.
Noise-reducing panels for highways and urban areas.
Thermal-insulating elements for energy-efficient buildings.
These advancements are positioning WPC as a premium, high-performance material rather than just an alternative to wood.
5. Expanding Application Scenarios
As technology progresses, WPC is finding new uses across various industries. Beyond construction, the material is gaining traction in sectors such as agriculture, logistics, transportation, automotive manufacturing, toys, shipbuilding, and even military applications.
For example:
In the automotive industry, WPC is being explored as a lightweight, durable alternative to conventional plastics for interior panels and trim.
In packaging and logistics, WPC pallets and crates offer a long-lasting, recyclable solution to traditional wooden and plastic options.
In agriculture, WPC is being used for irrigation channels, greenhouse structures, and animal enclosures, benefiting farmers and reducing environmental impact.
As new application scenarios continue to emerge, WPC will become an integral part of multiple industries, further increasing its global demand.
A Promising Future for WPC Materials
Wood-plastic composites are proving to be a game-changer in the materials industry. By offering durability, sustainability, and versatility, WPC is emerging as a preferred choice for environmentally conscious consumers, architects, and manufacturers.
As technology and manufacturing capabilities advance, WPC will become more efficient, cost-effective, and widely adopted. Governments and businesses alike are recognizing its potential to reduce deforestation, minimize plastic waste, and contribute to a circular economy.
With continuous innovation in raw materials, intelligent manufacturing, and high-value applications, WPC is set to redefine the future of sustainable materials. As a result, its role in reducing carbon footprints and promoting ecological balance will only grow stronger in the coming years.
Conclusion
In a world where sustainability is no longer an option but a necessity, WPC stands out as a revolutionary material. By aligning with global environmental goals, enhancing performance through technological advancements, and expanding its applications, WPC is positioned to become a cornerstone of the low-carbon economy.
For industries looking to build smarter, greener, and more efficiently, WPC is the future. Its journey has only just begun, and as innovation accelerates, its impact on the world will continue to expand—one eco-friendly product at a time.
Trending Reading
What Are the Differences Between the WPC Board and PVC Board?
[2025 Update] How Long Does WPC Decking Last?